RF Attenuator
DESCRIPTION
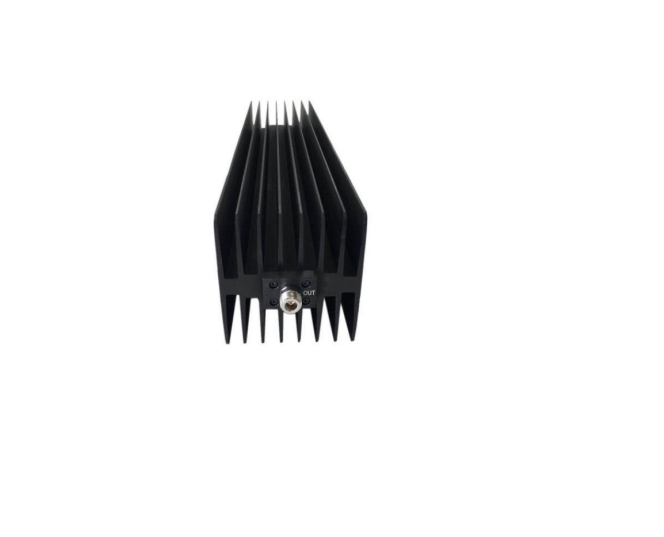
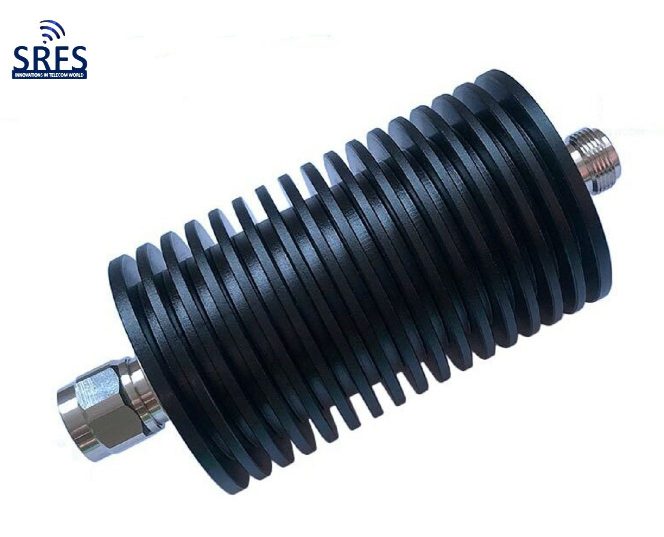
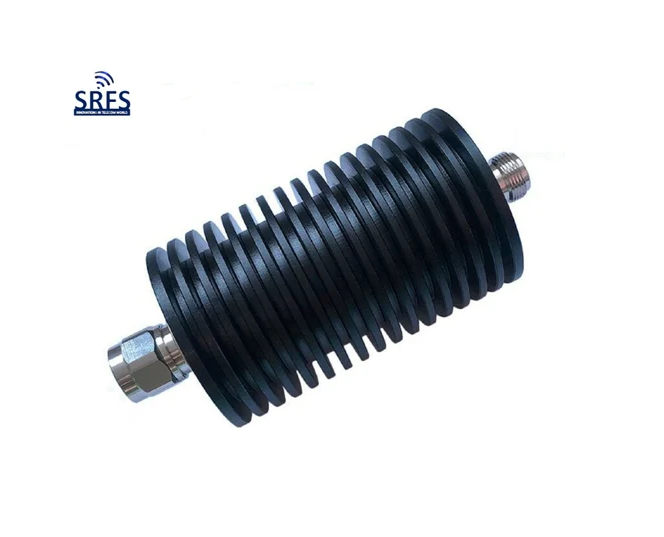
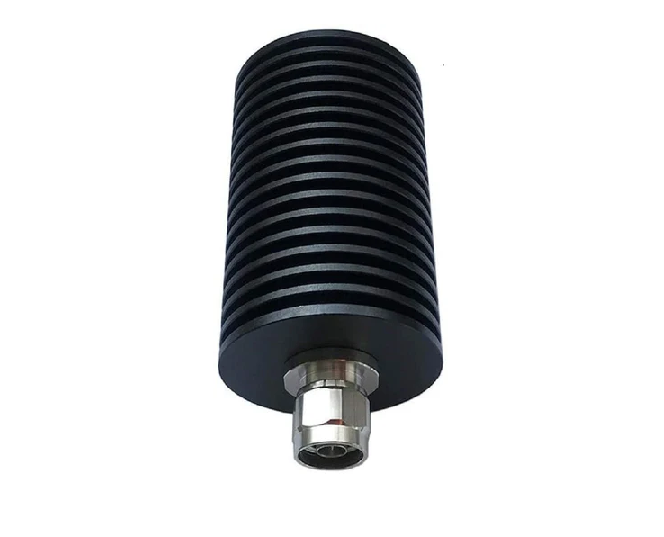
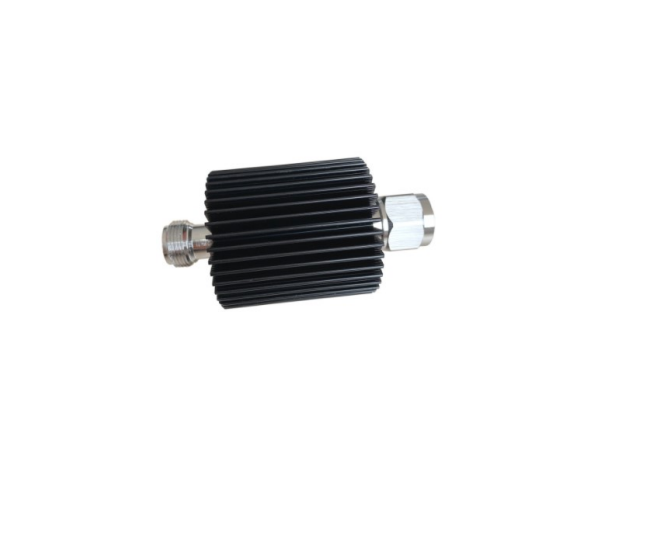
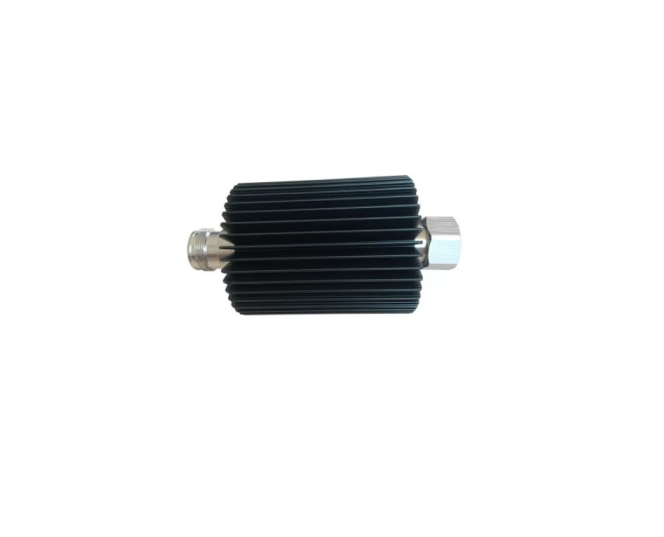
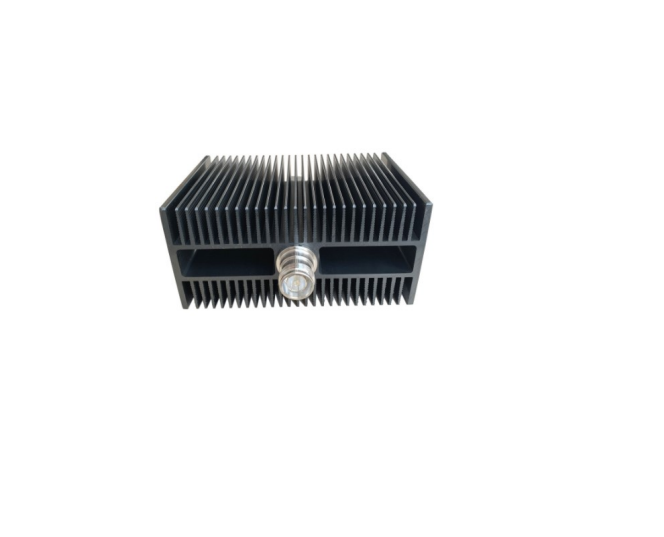
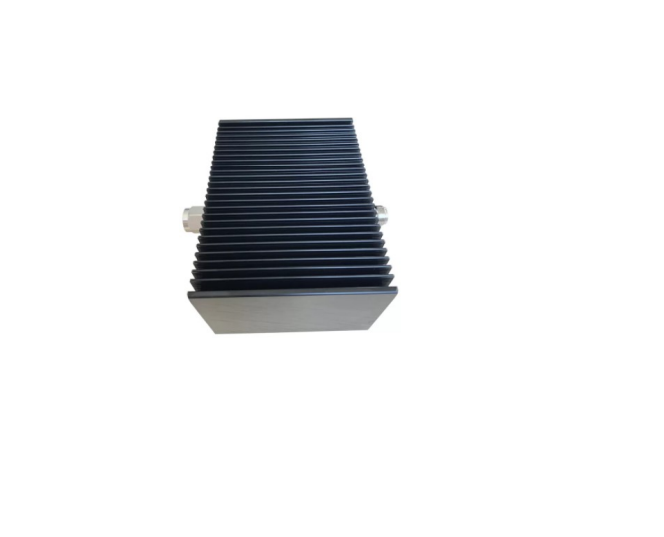
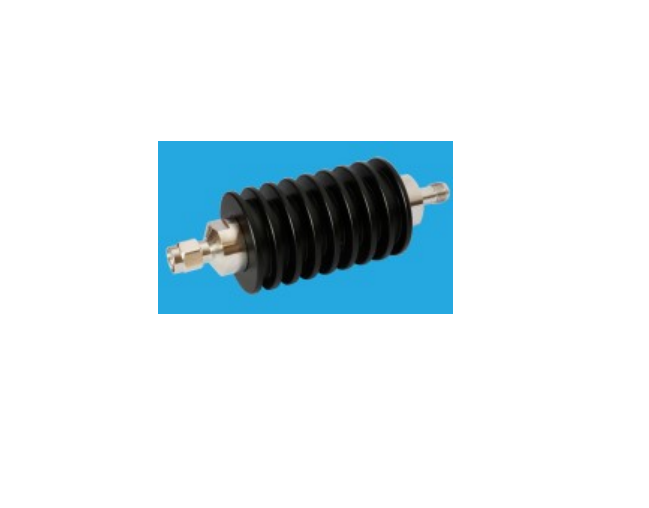
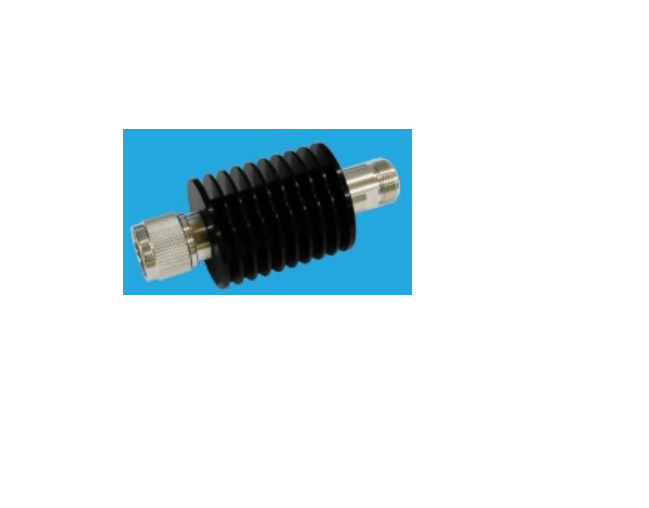
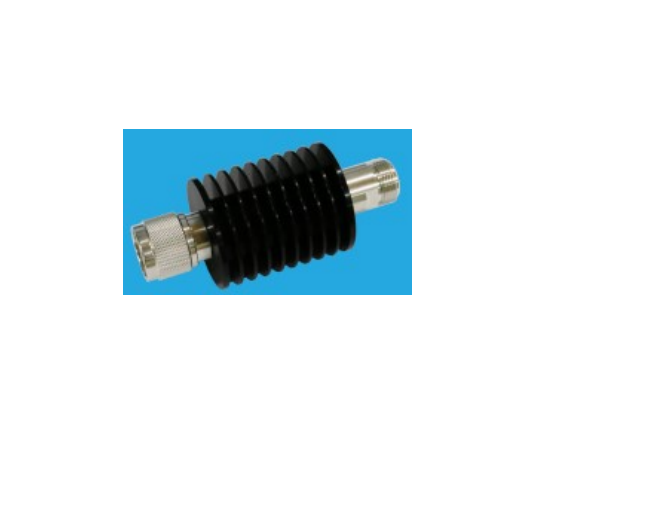
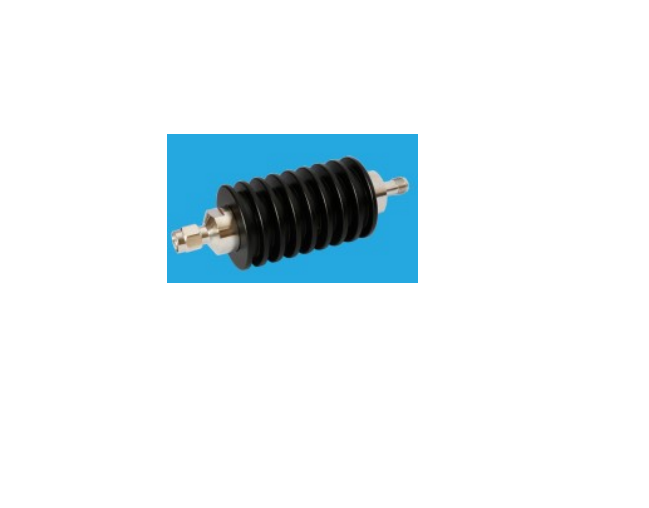
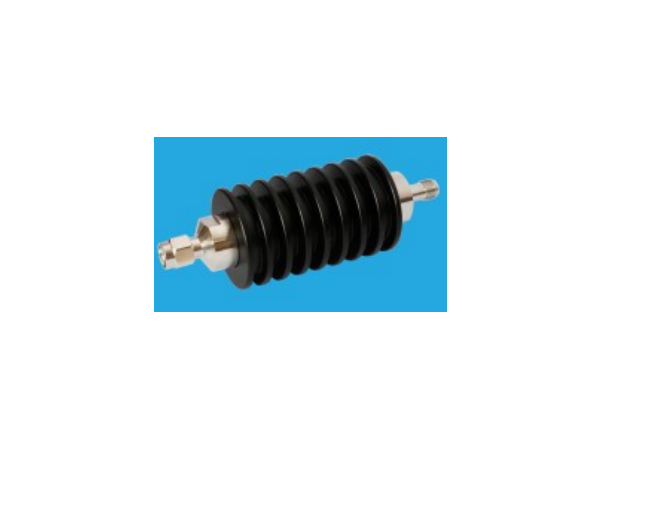
An RF attenuator, often referred to as an RF power attenuator, is a crucial component in the world of radio frequency (RF) electronics. Its primary purpose is to reduce the strength of an RF signal without introducing distortion or altering its waveform. RF attenuators find extensive use in various applications, including signal testing, calibration, and ensuring signal integrity in sensitive RF circuits.
These devices come in various forms, including fixed, variable, and step attenuators, providing flexibility in controlling signal power levels. Whether you’re working in telecommunications, RF testing, or amateur radio, an RF attenuator plays a vital role in maintaining precise control over signal strength for optimal performance and measurement accuracy.
SRFS Teleinfra hosts a thriving community of RF attenuator manufacturers & suppliers. These experts provide top-quality RF attenuators to meet diverse industry needs. Whether you require fixed or variable attenuators, count on India’s reliable RF attenuator manufacturers and suppliers for quality products and timely delivery.
FAQ's
1. What is an RF Attenuator?
An RF Attenuator is an electronic device used to reduce the power level of an RF signal without significantly distorting its waveform. It is commonly used in applications where precise control of signal strength is required, such as in testing and measurement, signal conditioning, and communication systems.
2. How does an RF Attenuator work?
An RF Attenuator works by introducing a specific amount of resistance into the signal path, thereby reducing the amplitude of the signal. This can be achieved through various designs, including fixed, variable, and step attenuators, which use resistive elements to achieve the desired level of attenuation.
3. What are the types of RF Attenuators?
There are several types of RF Attenuators, including:
Fixed Attenuators: Provide a constant level of attenuation.
Variable Attenuators: Allow adjustment of the attenuation level.
Step Attenuators: Offer discrete steps of attenuation, which can be selected manually or electronically.
Programmable Attenuators: Controlled digitally to provide precise attenuation levels.